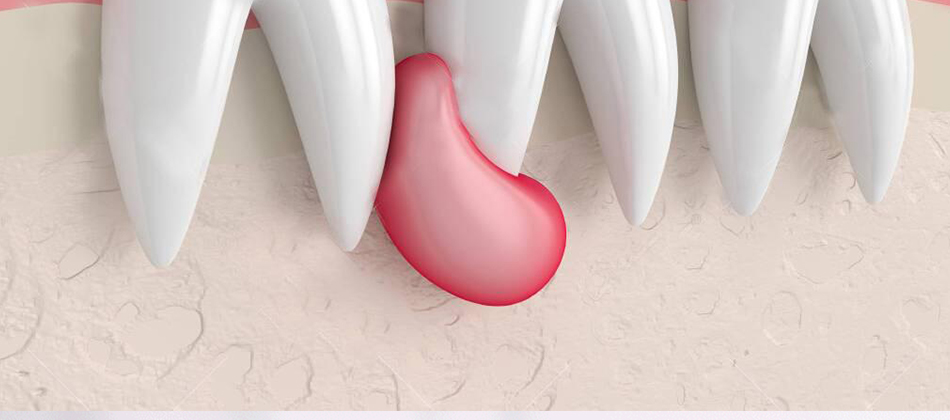
What is a Dental Cyst?
A dental cyst is the formation of a fluid-filled sac in the tissues around the tooth. Cysts that can form on tooth roots or gums are usually painless, but can cause tooth loss, bone loss and infection. If left untreated, they can grow and affect surrounding tissues, causing pain, swelling and other discomfort in the teeth.
What Causes Dental Cysts?
Dental cysts usually occur as a result of an infection at the root of the tooth. These infections can be caused by many factors, including tooth decay, gum disease, or damage to the tooth. Infection may occur when bacteria reach the pulp of the tooth and cause infection there. This infection can lead to inflammation that can lead to cyst formation. Dental cysts can also occur after trauma, genetic factors, or tooth extraction.
What Dangers Can a Dental Cyst Cause?
Dental cysts can pose several potential dangers. First, as they grow, they can put pressure on the bone tissue surrounding the teeth, which can lead to tooth loss. They can also become infected and the infection can spread, leading to more serious health problems. In rare cases, dental cysts may be cancerous or contain cancerous cells. Therefore, it is important to treat dental cysts as soon as possible.
What are the Symptoms of Dental Cysts?
Dental cysts can often grow without symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during dental X-rays or other imaging tests. However, in some cases, dental cysts can cause certain symptoms. These symptoms may include:
- Tooth pain or sensitivity
- Feeling of swelling or lump in the tooth
- Gum swelling or tenderness
- Signs of infection in the tooth or mouth, such as a bad smell, taste or swelling in the mouth
- Movement or shaking of the tooth
When these symptoms are noticed, it is important to consult a dentist.
What are the Types of Dental Cysts?
Dental cysts can be of different types and some of them are:
Radicular cysts: These are the most common dental cysts. They develop at the root of a previously infected tooth and often cause symptoms such as gingivitis, toothache, gum swelling and loosening of the tooth.Follicular cysts: These cysts usually develop in the tissues around impacted teeth in the jaw bones. They show symptoms such as gum swelling and pain.Lateral periodontal cysts: These cysts mostly develop in the gums near the tooth roots and are often painless. They are seen more rarely.Dentigerous cysts: These cysts are usually seen in people before the age of 20 and usually develop around an impacted tooth. They show symptoms such as toothache, swelling and shaking.Calcified cysts: These cysts are formed by the accumulation of calcium in cysts that were previously diagnosed as dental cysts.Dermoid cysts: Dermoid cysts are rare cysts that develop in the skin tissue near or around tooth roots.How to Treat Dental Cysts?
Treatment for dental cysts may vary depending on the type, size, location and symptoms of the cyst. Treatment of dental cysts can be done in the following ways:
Monitoring: Small dental cysts can usually be detected without any symptoms and do not require surgical intervention. In this case, the dentist will often monitor the growth of the cyst.Cyst removal: Large cysts may cause symptoms and require treatment. Surgical intervention may be required to remove the cyst. During the procedure, the cyst can be removed along with the surrounding tissues.Root canal treatment: In some cases, a dental cyst may occur due to infection in the tooth. In this case, root canal treatment may be required to treat the infection caused by the cyst.Tooth extraction: If the dental cyst originates from the root of the tooth, the tooth may need to be extracted. After tooth extraction, the cyst usually heals on its own.Marsupialization: In large cysts, it may not be possible to completely remove the cyst. In this case, marsupialization, a procedure in which the cyst cavity is left open, can be applied. This procedure may help reduce the size of the cyst and allow it to be removed completely later.The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size of the cyst, its location, and the severity of its symptoms. Therefore, it is important to consult a dentist for treatment of dental cysts.
What is the Recovery Process After Cyst Operations?
The healing process after cyst operations may vary depending on the size, location and treatment method of the cyst. Usually, there may be pain, swelling and bleeding in the first few days after the surgical procedure. The recovery process may vary depending on the type of surgery, the size and location of the cyst, and the patient’s age and health condition.
Things to do during the recovery process:
- After the surgical operation, it is very important to use painkillers and antibiotics as recommended by the doctor.
- Liquid and soft foods should be consumed for the first few days. Consuming hot or cold foods should be avoided.
- Mouth washing should not be done in the first 24 hours after the operation. A toothbrush should not be used.
- No objects should be inserted into the mouth for 24 hours after the operation.
- Habits such as smoking and alcohol should be abandoned for at least 24 hours after the operation.
- Cold application can be applied to the operation area. A towel wrapped in an ice pack or a cold compress can be used.
- Physical activities, especially activities around the mouth, should be kept to a minimum for 48 hours after the operation.
Post-operative checks are important for the success of the surgical procedure. Usually the first follow-up appointment takes place a few days later. During these checks, the doctor will give information about medication recommendations to relieve pain, the condition of the wound area, the condition of the stitches and other problems. Once the healing process is complete, patients can continue their normal dental care routine.